Nutrition Facts of Steak: A quick guide to understanding steaks.
Nutrition Facts of Steak: Nutrition facts of steak show that steaks are loved for their rich flavor and high protein content. But there’s more! Steaks are packed with nutrients that support your health and keep you satisfied. Curious about plant-based options? Check out our guide on vegan nutrition and its health benefits. In this guide, we dive into the nutrition facts of steak, covering the nutrients in different steak cuts, how cooking methods affect nutrition, and the benefits of adding steak to your diet. Also, find our home workout routine for beginners to keep your diet balanced with physical activity.
What Exactly Are the Nutrition Facts of Steak?
Steak is primarily beef but also includes other meats like buffalo and venison that fans call “steak.” Popular beef cuts include ribeye, sirloin, tenderloin, T-bone, and flank steak. For more information on different types of beef, you can visit Beef. It’s What’s For Dinner. Each of these cuts offers a unique combination of flavor, tenderness, and nutritional value.
Each cut has unique flavors and textures depending on the animal’s age, diet, and muscle type. A well-fed, well-aged cow produces a marbled, flavorful steak, while leaner cuts are ideal for those limiting fat. For balanced diet tips, visit our Nutrition section for recipes and guidance.
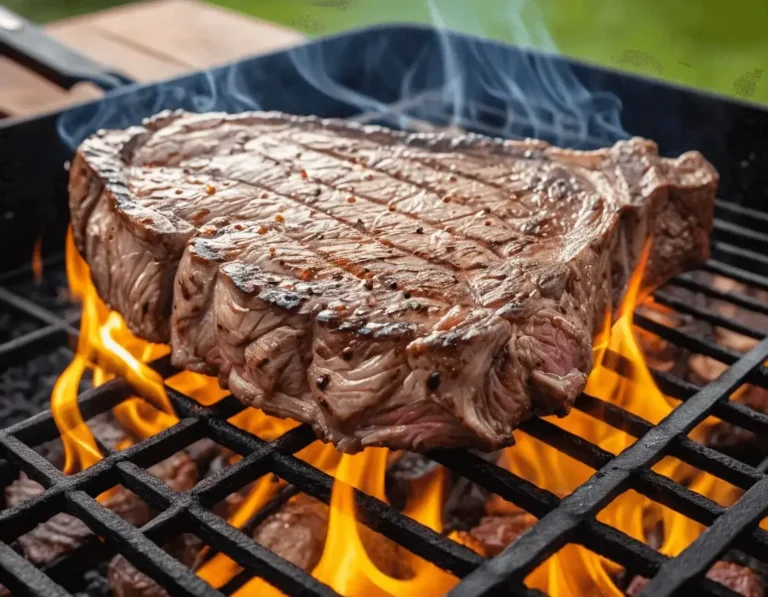
The way you cook steak affects both its taste and the nutrition facts of steak. Knowing these details can enhance your meal while keeping it healthy. For more insights into mental health, explore our tips on boosting mental wellness. To learn about maintaining a healthy lifestyle, check out our Healthy Living category for practical advice. Whether you grill, broil, or pan-fry, each method adds unique flavors while impacting the nutrition of your steak.
Nutrition Facts of Steak Breakdown
Inspecting the nutrition facts of steak, specifically a cooked 3-ounce serving, offers insights across the board, from ribeye to sirloin. The nutrients in steak provide numerous benefits for the body, from muscle maintenance to boosting the immune system.
| Nutrient | Amount per 3-Ounce Serving |
|---|---|
| Calories | 180-250 |
| Protein | 22-28 grams |
| Total Fat | 7-12 grams |
| Saturated Fat | 3-6 grams |
| Monounsaturated Fat | 3-5 grams |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | 0.5-2 grams |
| Cholesterol | 60-80 mg |
| Iron | 2-3 mg (10-15% DV) |
| Zinc | 4-6 mg (30-50% DV) |
| Vitamin B12 | 1-2 mcg (40-80% DV) |
| Selenium | 15-30 mcg (20-55% DV) |
Bear in mind that the nutrition facts of steak vary with the cut and preparation style. Remember, sides and sauces can also alter steak’s nutrition. For example, adding a butter-based sauce will increase the fat content significantly, while pairing your steak with a fresh salad will balance out your meal.
A Slice of Different Steaks
Delve into the individuality of various steaks:
Ribeye Nutrition Facts
- A heavyweight in taste and tenderness.
- Calories: ~290
- Protein: Roughly 25 grams
- Fat: Near 22 grams
- Saturated Fat: 9 grams
- Grilling this one heightens its impressive flavors. Its marbling makes it one of the most flavorful cuts, but also one of the more caloric. Ideal for those indulgent occasions when flavor is the priority.
T-Bone Steak Nutrition Facts

- A feast for the taste buds and a beast for hunger.
- Calories: ~200
- Protein: 24 grams
- Fat: Roughly 12 grams
- Saturated Fat: 5 grams
- A tender yet gutsy flavor-profile is the hallmark here. The T-Bone offers both tenderness and flavor due to the combination of tenderloin and strip steak cuts. It is perfect for grilling, and its size makes it a satisfying meal.
Filet Mignon Nutrition Facts

- Softness? Check! It’s filet mignon.
- Calories: 240
- Protein: 26 grams
- Fat: 16 grams
- Saturated Fat: 7 grams
- Rich and refined, designed for special occasions. Filet mignon is one of the most tender cuts of beef, and its delicate flavor and soft texture make it a favorite for celebrations and special dinners. It pairs well with red wine and light sides.
Flank Steak Nutrition Facts
- A go-to for the health-aware.
- Calories: ~160
- Protein: 26 grams
- Fat: 5 grams
- Saturated Fat: 2 grams
- Marinate and grill for extraordinary zest. Flank steak is lean and full of flavor, making it a healthier option that doesn’t skimp on taste. It works well in stir-fries, fajitas, or salads, and its versatility is perfect for those looking to maintain a balanced diet.
Sirloin Nutrition Facts
- Tasty and wallet-friendly.
- Calories: ~210
- Protein: 24 grams
- Fat: 10 grams
- Saturated Fat: 4 grams
- Customizable to many cooking approaches. Sirloin is known for its balance of flavor and leanness, making it a popular choice for weeknight meals. It can be grilled, broiled, or pan-fried and pairs wonderfully with a variety of side dishes, from roasted vegetables to mashed potatoes.
Solid Reasons to Chow Down on Steak
Protein Galore
- For fitness enthusiasts, steak is a muscle-building ally. Protein is essential for muscle repair and growth, and steak provides all the essential amino acids needed by the body. Including steak in your diet helps maintain muscle mass, especially when combined with regular exercise.
Packed with Iron
- The heme iron in steak is a boon for blood health, especially for those feeling run down. Iron is crucial for carrying oxygen in the blood, and the heme form found in red meat is more easily absorbed than the non-heme iron in plant sources. This makes steak an excellent choice for those who are prone to anemia or have higher iron needs, such as athletes and menstruating women.
Brimming with Nutrients
- Steaks teem with health-bolstering elements:
- Zinc: Boosts immune system. Zinc is vital for immune function, wound healing, and DNA synthesis. A serving of steak provides a significant portion of your daily zinc needs.
- Vitamin B12: Key for nerve function and energy. Vitamin B12 is essential for red blood cell formation, neurological health, and energy production. Steak is a major source of this vital vitamin, which is otherwise difficult to obtain from plant-based foods.
- Selenium: Important for thyroid health. Selenium plays a key role in metabolism and thyroid function. Regular consumption of steak can help you meet your daily selenium requirements, contributing to a healthy thyroid and proper metabolic function.
Muscles Dig It
- Steak’s amino acids are gym-goers’ friends, aiding in strength and recovery. For more information on fitness and muscle-building, explore our Fitness Tips section to complement your diet with effective workout strategies. Amino acids like leucine are particularly important for muscle protein synthesis, making steak an ideal choice for post-workout meals. It provides not only protein but also nutrients that help reduce muscle soreness and promote faster recovery.
Warning Signs
Despite its tasty allure, moderation in consuming steak is crucial. Overindulging in red meat can have health implications, and it is important to balance it with other sources of protein and nutrients.
Fatty Business
- Steer clear of excessive saturated fat and unhealthy toppings. Some cuts of steak are high in saturated fat, which can contribute to elevated cholesterol levels if consumed in excess. Opt for lean cuts and avoid heavy butter sauces to keep your meal heart-healthy.
Linked to Disease?
- Heavy red meat eating may pose health risks. Watch your portions. Studies have suggested a potential link between high consumption of red meat and certain health conditions, such as cardiovascular disease and colorectal cancer. To learn more, visit the American Heart Association. Moderation is key—limit red meat to a few times a week and balance your diet with plant-based proteins.
Ecological Footprint
- The environmental impact of beef production is non-negligible. Try mixing protein sources for variety and responsibility. Beef production requires significant resources, including water and land, and contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. To reduce your environmental footprint, consider alternating between steak and more sustainable protein options like poultry, fish, or legumes.
Cooking’s Nutritional Impact
The cooking method chosen affects steak’s healthiness. Some cooking methods preserve nutrients better, while others can add unwanted calories or reduce nutritional value.
Grilling
- Strips away extra fat while locking in flavor. Grilling is a popular method that allows excess fat to drip off, making the steak leaner. However, be mindful of potential carcinogens formed by high-temperature cooking—use a marinade to reduce these risks.
Pan-Frying
- A tricky method. Aim for light oil use and controlled temperatures. Pan-frying can add extra calories if too much oil is used, but by using healthy fats like olive oil and keeping the temperature moderate, you can achieve a delicious and healthy meal.
Broiling
- A great alternative for juiciness and caramelizing without the added fat. Broiling cooks steak quickly at high temperatures, which helps retain juices and enhances flavor. It’s a great option for achieving that perfect crust without adding extra oils or fats.
The nutrition facts of steak show that it stands at the intersection of dietary pleasure and well-being. Prioritize balance, diversify your plate, and feast on steak in moderation to preserve health. Selection is everything; pick what’s good for both palate and body. Enjoy the journey steak takes your taste buds on!
FAQ – Discover the Complete Nutrition Facts of Steak
- What are the key nutritional components of steak?
Steak is a rich source of protein, essential amino acids, iron, zinc, and B vitamins. It also contains varying levels of fat, including saturated and unsaturated fats, depending on the cut. These components are vital for overall health, including muscle maintenance, immune function, and energy production. - How does the nutritional value of different cuts of steak vary?
Different cuts of steak have varying amounts of fat and calories. For example, ribeye is more fatty and caloric than sirloin, making it richer in flavor but also higher in calories. Leaner cuts like flank and sirloin are better options for those looking to reduce fat intake while still enjoying steak. - Is steak a good source of iron?
Yes, steak is an excellent source of heme iron, which is more easily absorbed by the body compared to non-heme iron found in plant sources. This makes it beneficial for those who need to boost their iron intake, such as individuals with anemia, athletes, or those on menstruation. Iron from steak helps in oxygen transportation and energy levels. - How can I choose a healthier steak option?
To choose a healthier steak option, look for lean cuts, such as flank, sirloin, or tenderloin. Additionally, trimming visible fat and opting for grass-fed varieties can also enhance the nutritional value. Grass-fed beef tends to have more omega-3 fatty acids, which are beneficial for heart health. Consider pairing your steak with vegetables to create a balanced and nutrient-dense meal.







One Comment